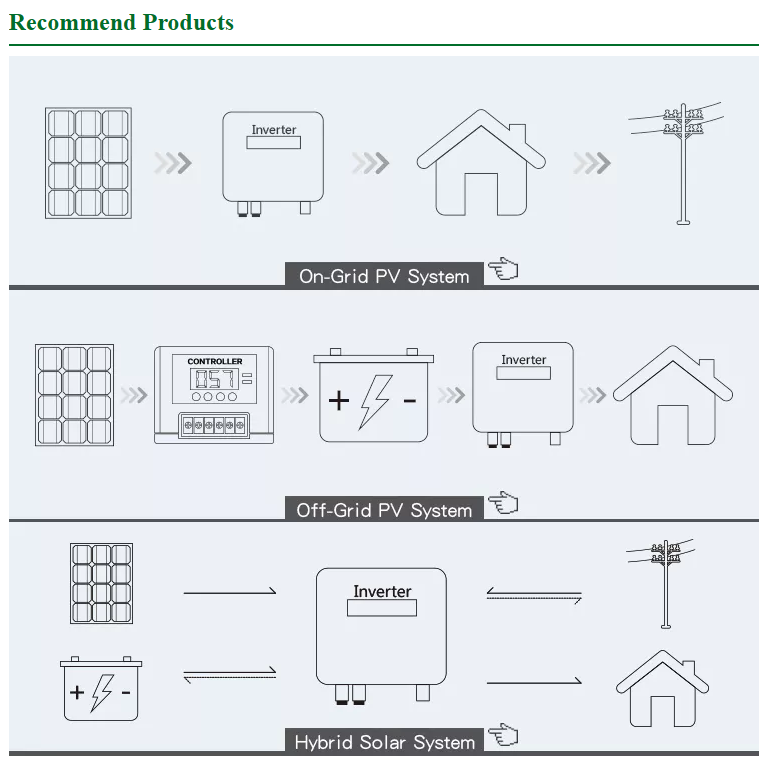
Solar photovoltaic (PV) power systems can be broadly classified into two categories based on their relationship with the power grid: stand-alone PV systems and grid-connected PV systems.
Stand-alone PV System:
A stand-alone PV system consists of a solar PV array, battery bank, charge controller, power electronic converter (inverter), and loads. The system operates by converting solar radiation into electricity through the PV array, which is then supplied to the loads after being transformed by the power electronic converter. Excess electricity generated is stored in the battery bank through the charge controller. This allows for the usage of stored energy during periods of insufficient sunlight. The stored energy can be converted into AC power at 220V and 50Hz using the power electronic inverter, filtering, and frequency transformation, thereby supplying AC loads. Stand-alone PV systems require energy storage components, primarily in the form of batteries, since solar power generation occurs during the day while loads may require power throughout the day.
Grid-connected PV System:
A grid-connected PV system consists of a PV array, high-frequency DC/DC boost circuit, power electronic converter (inverter), and system monitoring components. The system operates by converting solar radiation through the PV array, followed by high-frequency DC conversion to high-voltage DC. The power is then inverted by the power electronic inverter to generate sinusoidal AC current that matches the grid voltage. The generated AC power is fed into the utility grid. The key difference between grid-connected PV systems and stand-alone systems is that grid-connected systems are directly connected to the power grid, allowing surplus electricity from the PV array to be supplied to the grid. This eliminates the need for energy storage components such as batteries, reducing system costs and ensuring reliability. Additionally, during the summer when solar radiation is high and PV system output is abundant, grid-connected systems can help regulate peak loads on the grid. With the widespread adoption of solar PV systems and the rapid decline in solar cell prices in recent years, grid-connected systems are expected to be increasingly utilized.
Overall, grid-connected PV systems offer advantages such as cost savings, enhanced reliability, and the ability to contribute excess electricity to the grid, making them more widely applicable.
Post time: Jul-28-2023